
- Credit
- Raven Eye Photography
- Credit
- Jim Steenburgh
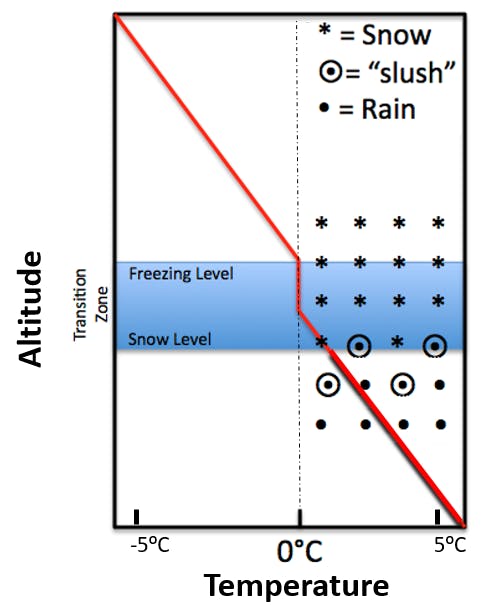
The snow level is the altitude at which precipitation changes from snow to rain. How far below the freezing level it is located depends on the amount of cooling that takes place due to sublimation and melting.
If the air mass is dry in the low levels, falling snow will sublimate (change from frozen water to water vapour) and cool the atmosphere. The snow level will quickly plummet from near the freezing level to several hundred metres below.
If the atmosphere is moist, little cooling from sublimation will occur but melting snow (which also cools the atmosphere) still occurs. The harder it is precipitating, the more melting occurs, leading to greater cooling and lowering of the snow level.
A general rule of thumb to determine snow level is to subtract 200-300m from the freezing level, but depending on the atmospheric conditions, snow level may be substantially lower.
See also: