- Credit
- Nolan Atkins (Lyndon State College)
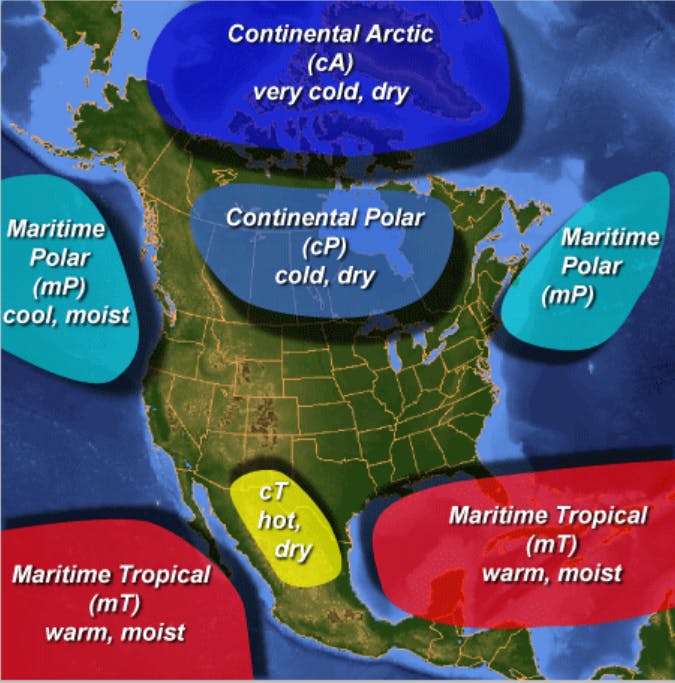
An air mass is a large region of air with minimal horizontal variation in temperature and moisture. An air mass forms when air remains stationary for enough time (usually many days or weeks) to exchange energy (absorbing heat or cooling) and moisture with the surface below.
Air masses are classified in two ways, based on where they originated:
- By moisture: Air masses that form over land are called continental (dry), while ones that form over oceans are called maritime (moist).
- By temperature: Whether they are from tropical (warm), polar (cold) or arctic (extremely cold) regions.
There are a total of six air mass types: continental tropical (cT), maritime tropical (mT), continental polar (cP), maritime polar (mP), continental arctic (cA), and maritime arctic (mA). Maritime arctic air masses affect BC’s coast when continental arctic air pushes through coastal fjords. Strong to very strong northerly/northeasterly outflow winds occur and localized bands of heavy snow (known as streamers) pummel communities and mountains downstream (e.g. eastern Vancouver Island).