- Crédit
- NOAA NWS
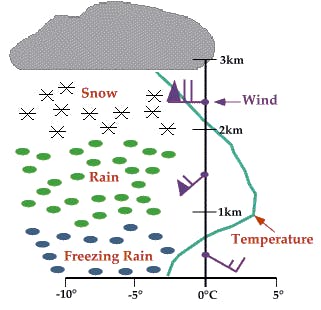
An above freezing layer (AFL) is a horizontal layer of air at some altitude in the atmosphere with a temperature above 0 C. It lies between two layers of sub-freezing air. AFLs are a common result of atmospheric subsidence and incoming warm fronts overriding cold air entrenched within valley bottoms. A temperature inversion is always present at the bottom of the layer.
Note that warm air at valley bottom is not referred to as an above freezing layer because air is normally warmest at low elevations.
Elevated layers of above freezing air play an important role in the type of precipitation observed at a given altitude. Above an AFL, precipitation falls as snow. It then transitions to rain within the AFL (assuming the layer is of sufficient depth), and then to ice pellets or freezing rain below the AFL.