
- Credit
- Versageek/Wikipedia Creative Commons
- Credit
- Brockmann Consult
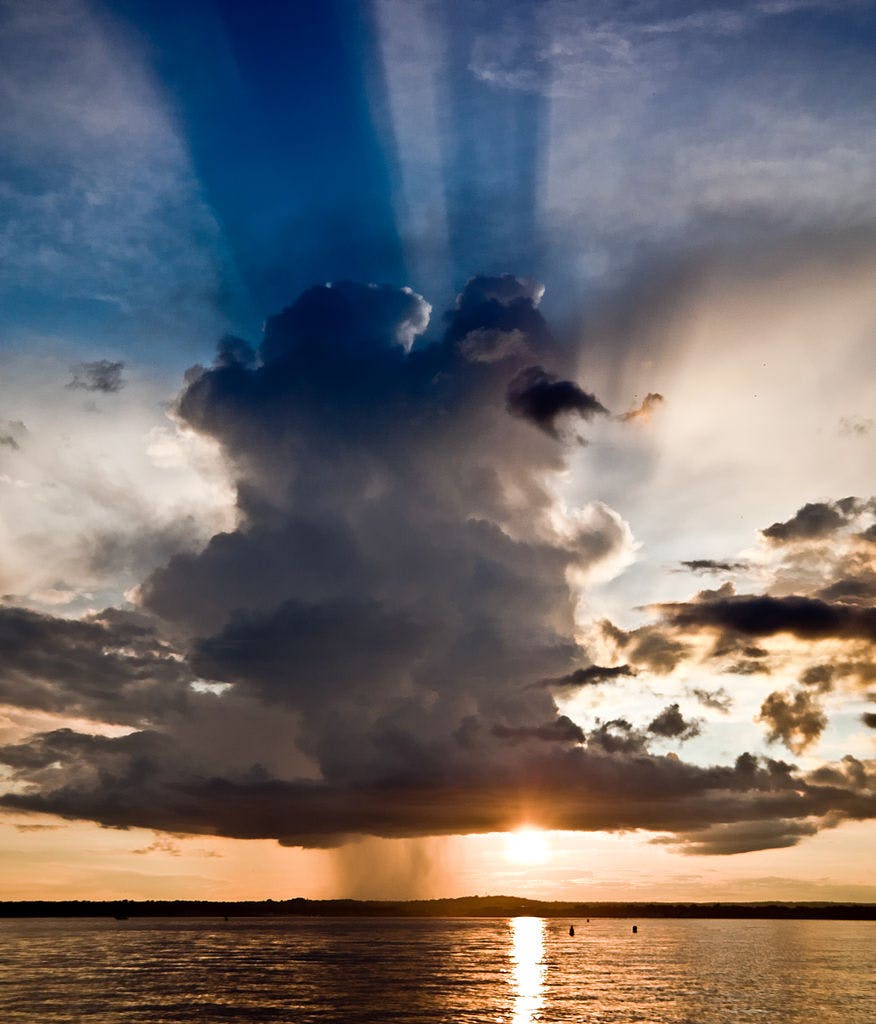
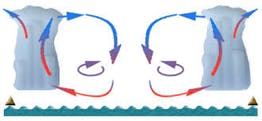
Convection is the vertical movement of air in which warm air rises (picture bubbles rising to the top in a boiling pot of water) and cool air sinks. Like other forms of atmospheric lift, convective lift causes rising air to cool and reach saturation, forming tall clouds and showery precipitation. Precipitation resulting from convective storms is known for being variable in location and duration, with locally intense, short-bursts of precipitation possible. This, in turn, creates greater uncertainty in forecasting precipitation.
Strong convective lift can result in very tall cloud formations called cumulonimbus clouds, which are associated with thunder and lightning.
See also: