- Credit
- Wikihow.com, modified by Lisa Erven
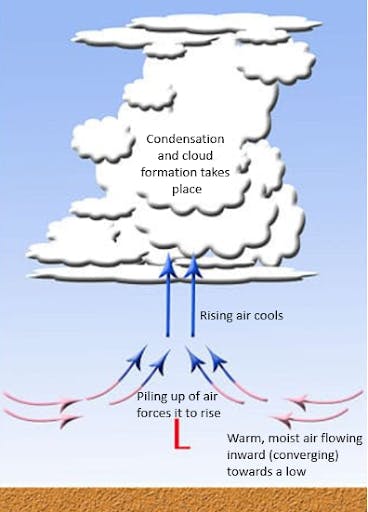
Atmospheric convergence refers to two or more streams of air flowing into one another, or when stronger winds flow into slower winds. This piling up of air at low levels of the atmosphere results in atmospheric lift, or rising air. As air converges and lifts, cooling takes place, leading to condensation, cloud formation and, ultimately, precipitation.
Atmospheric convergence is one of the key processes involved with storm development and precipitation. In the mountain environment, convergence occurs on windward slopes and at the heads of valleys and fjords, leading to stronger winds and enhanced precipitation in those locations.